
Pythagorean Theorem Part 1 Proof Finding A Missing Side Ck 12 Foundation
By Richard updated on Leave a Comment on What Is The Rule Of Pythagoras Theorem The 3 4 5 Rule For Squaring This Is A Carpenter S Method For Getting A Perfect Square Based On The Pythagorean 3 4 5 Rule Pythagorean Theorem Perfect SquaresThe converse of the Pythagorean theorem is a rule that is used to classify triangles as either right triangle, acute triangle, or obtuse triangle Given the Pythagorean Theorem, a 2 b 2 = c 2, then For an acute triangle, c 2 <
Pythagorean theorem and 3 4 5 rule
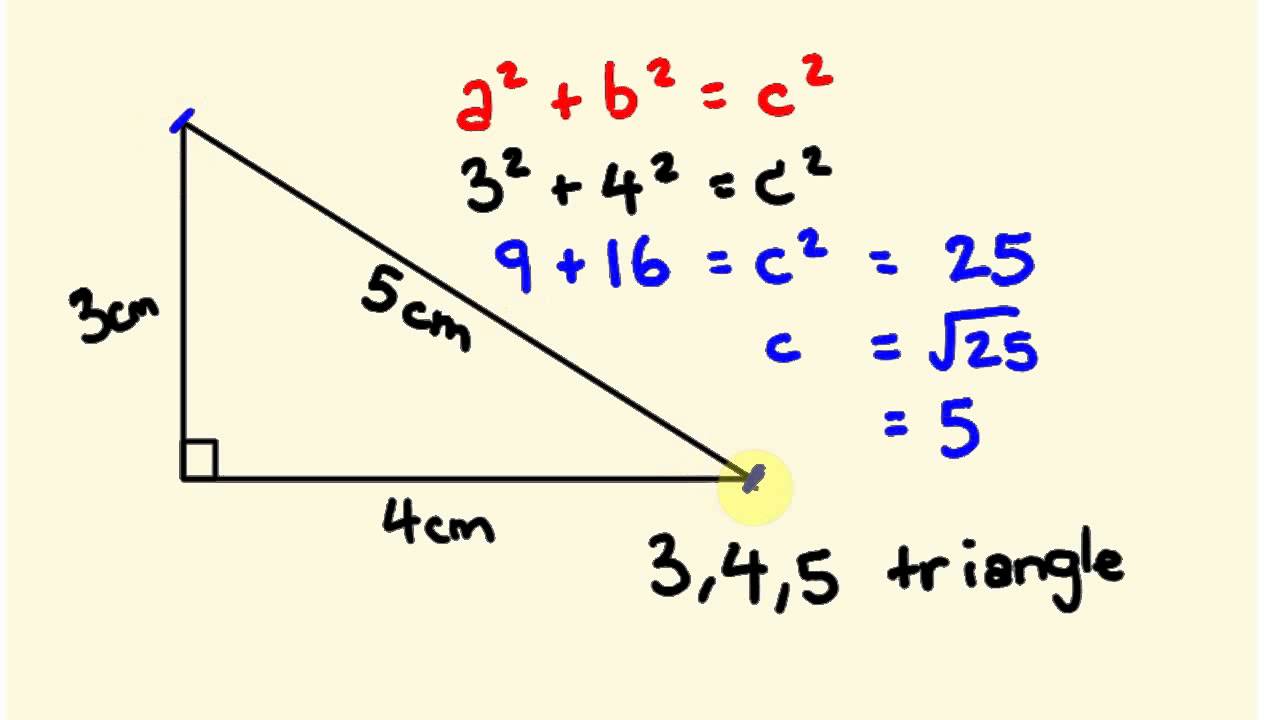
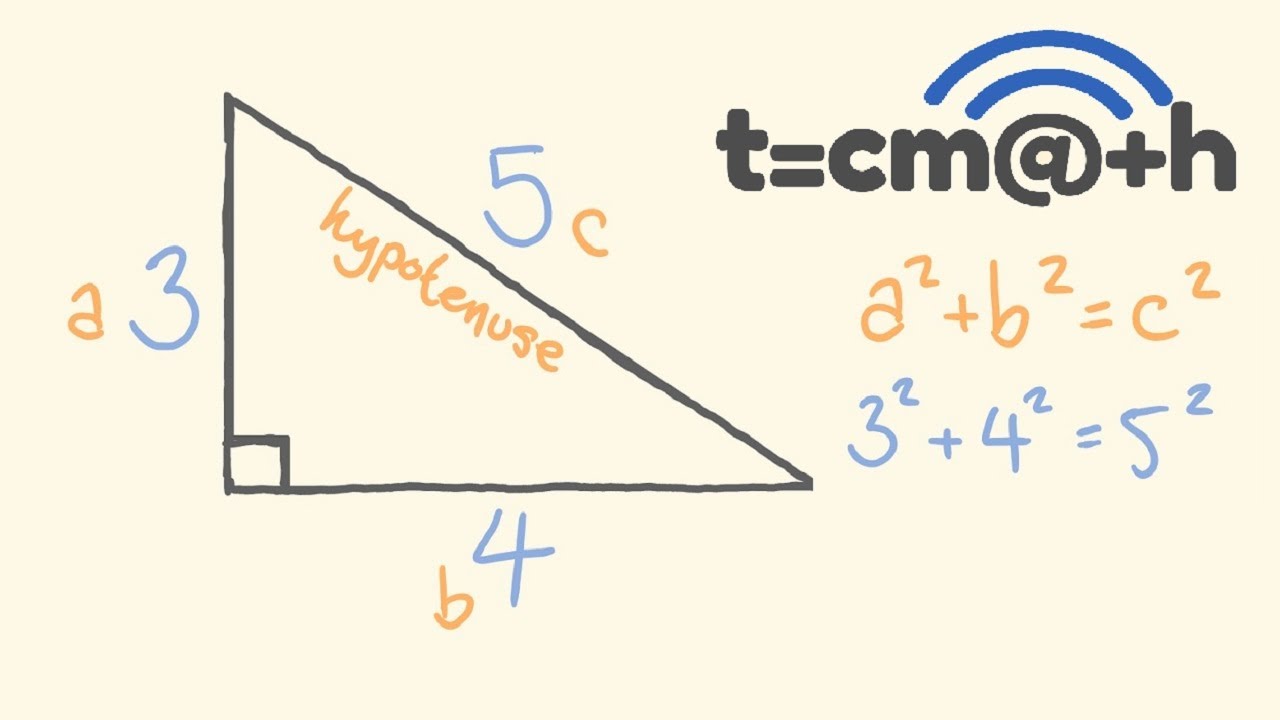
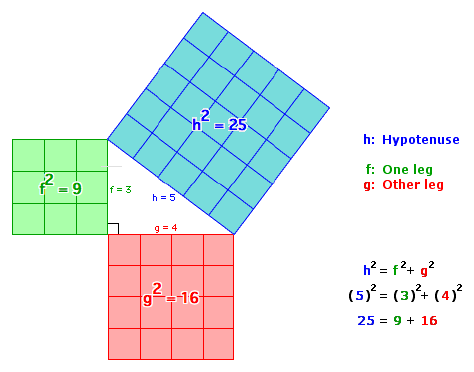
Pythagorean theorem and 3 4 5 rule-Draw an arc 400 away from the start of the 300 line Draw an arc 500 away from the end of the 300 line Connect from the start of the 300 line to where the arcs cross And you have your 3,4,5 triangle with its right angleA Pythagorean triple is a set of 3 positive integers for sides a and b and hypotenuse c that satisfy the Pythagorean Theorem formula a 2 b 2 = c 2 The smallest known Pythagorean triple is 3, 4, and 5 Showing the work
Pythagorean Theory Ppt Download
3 , 4 , 5 {\displaystyle 3,4,5} The reciprocal Pythagorean theorem is a special case of the optic equation 1 p 1 q = 1 r {\displaystyle {\frac {1} {p}} {\frac {1} {q}}= {\frac {1} {r}}} where the denominators are squares and also for a heptagonal triangle whose sides pPythagorean Triples The general formula for Pythagorean triples can be shown as, a 2 b 2 = c 2, where a, b, and c are the positive integers that satisfy this equation, where 'c' is the hypotenuse or the longest side of the triangle and a and b are the other two legs of the rightangled triangleThe Pythagorean triples are represented as (a,b, c) The most popular example of PythagoreanThe Pythagorean Theorem tells us that the relationship in every right triangle is a 2 b 2 = c 2 Example C 2 = 6 2 4 2 C 2 = 36 16 C 2 = 52 C = 52 C ≈ 72 There are a couple of special types of right triangles, like the 45°45°
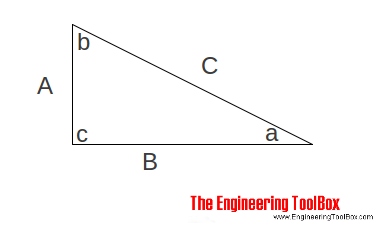
The cosine rule, also known as the law of cosines, relates all three sides of a triangle with an angle of a triangle The Law of Cosines is the extrapolation of the Pythagorean theorem for any triangle Pythagorean theorem works only in a right triangle Pythagorean theorem is a special case of the Law of Cosines and can be derived from itAnswer (1 of 5) As the other answers show, you can make an endrun around Pythagoras' Theorem, and there are plenty of ways to do it The cosine rule is really a generalisation of Pythagoras' Theorem, and is usually proved using Pythagoras as a startingpoint Trigonometry is almost always deve3,4,5 rule / Pythagoras Theorem This video gives a simple read world example to explain the concept Suitable for learners new to the conceptNarrated by a
Pythagorean theorem and 3 4 5 ruleのギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | 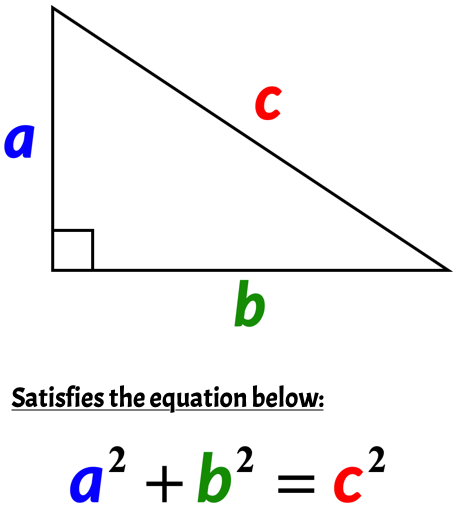 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | 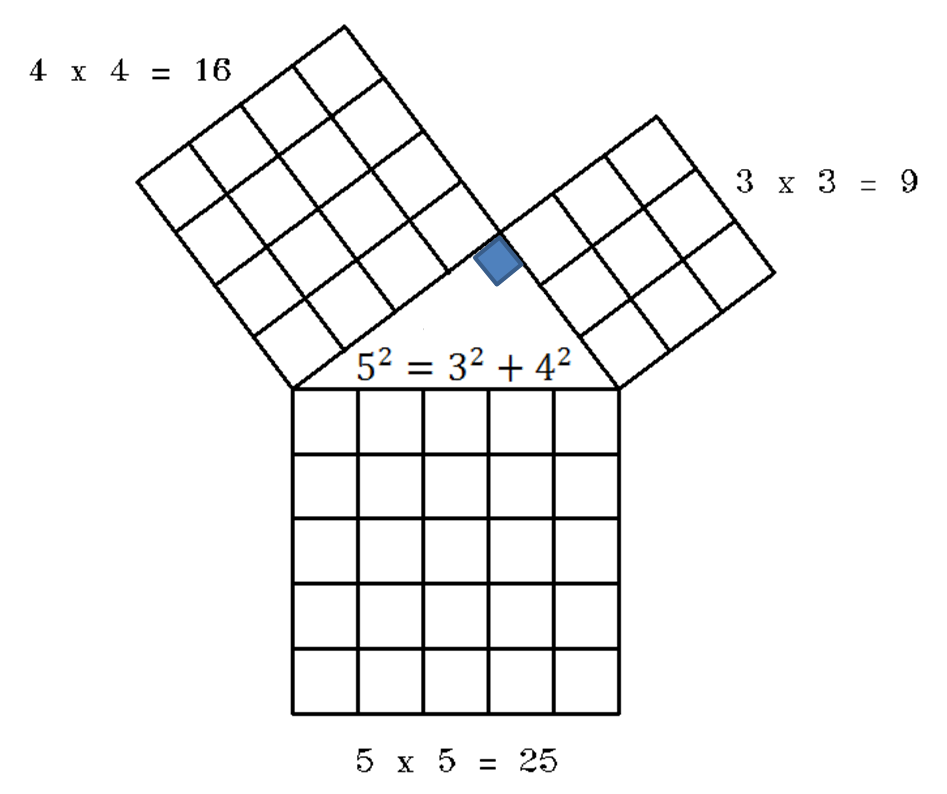 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | 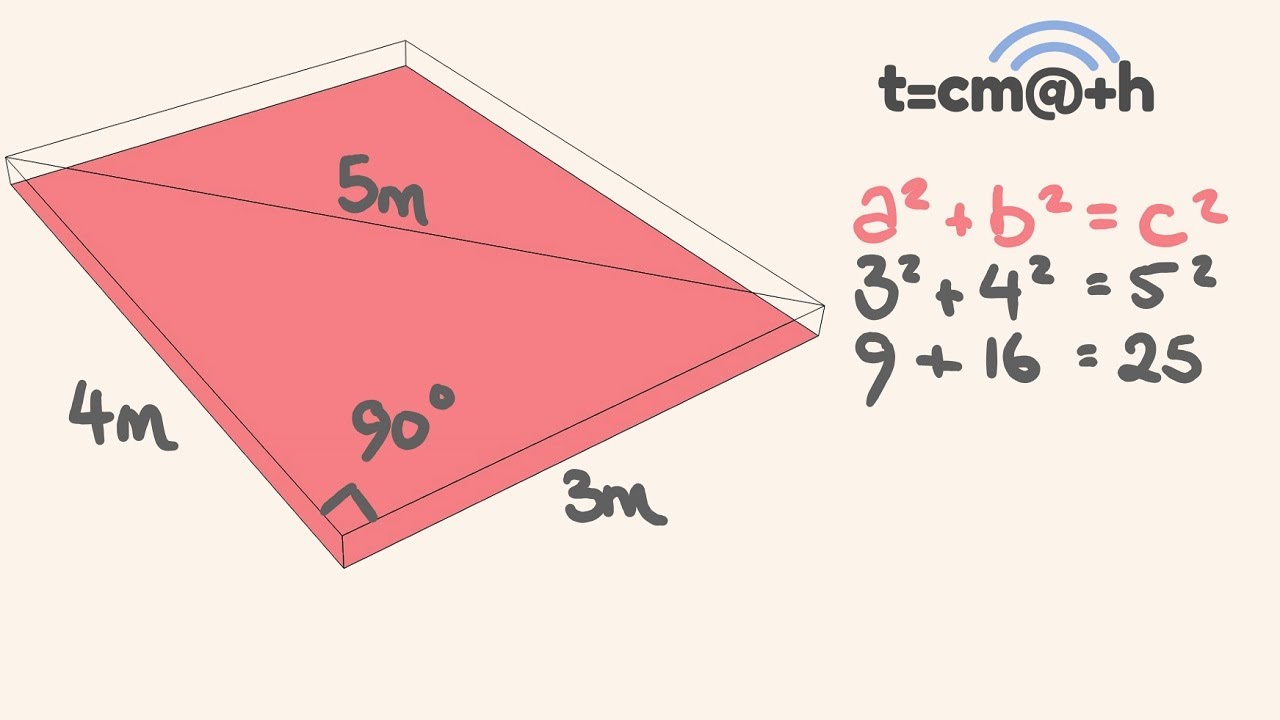 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | 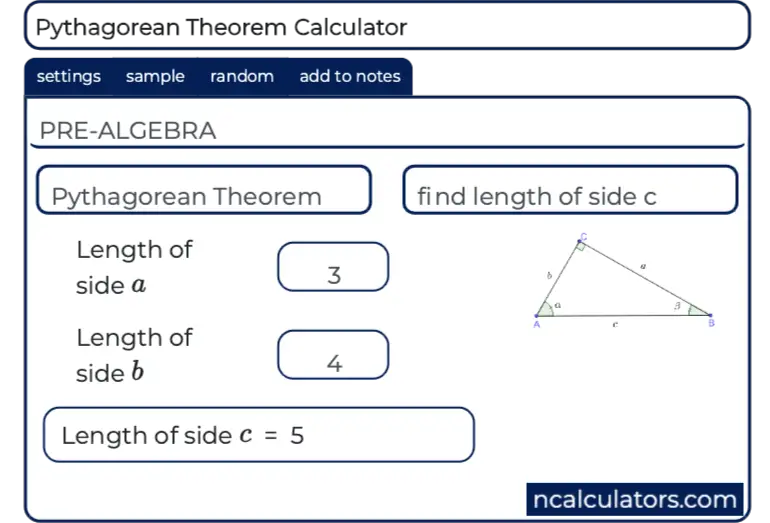 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
/51238812-copy-56aa2c5a3df78cf772acf93e.jpg) S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | 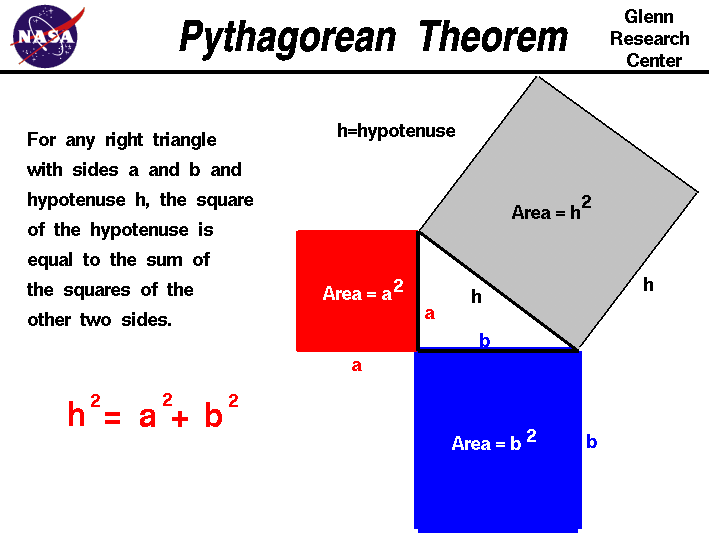 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | 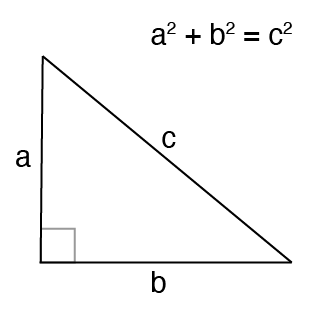 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | 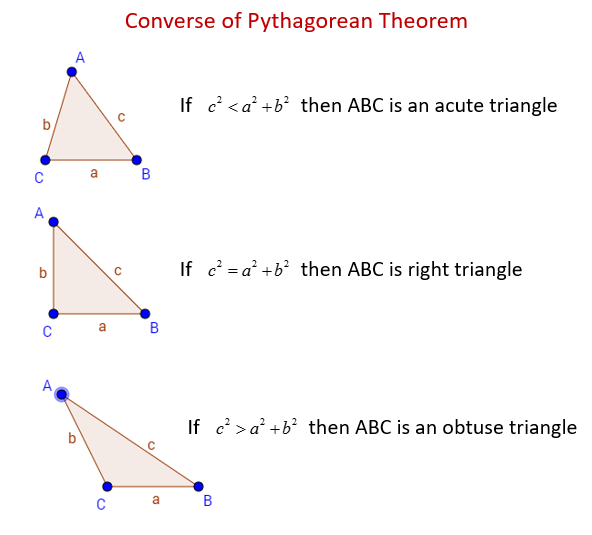 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
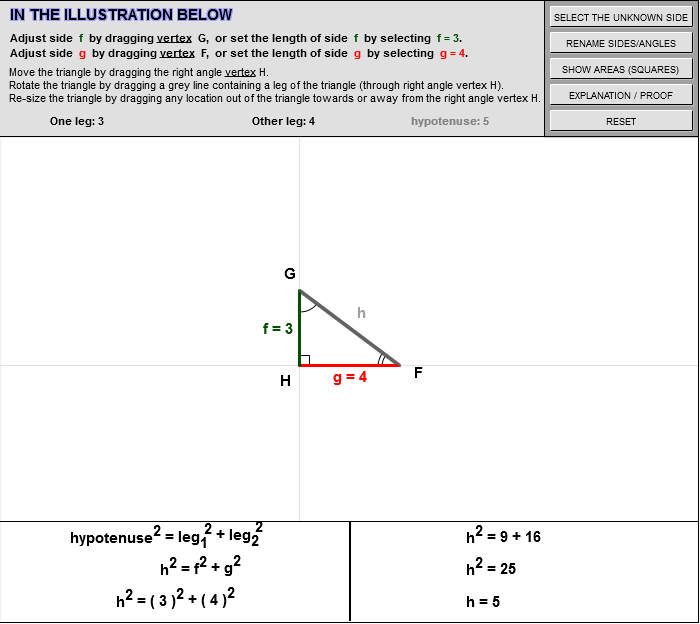 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | 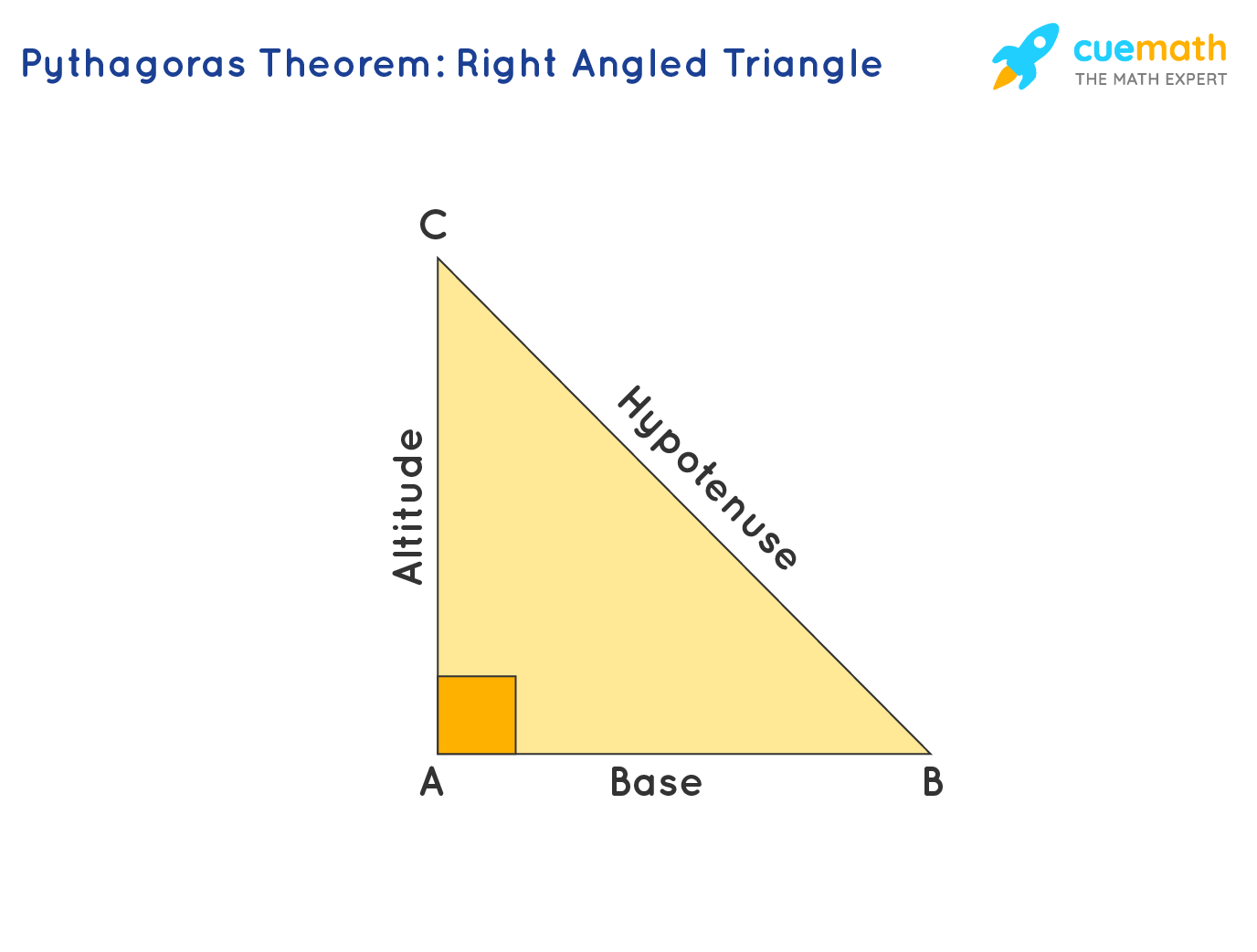 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/19524905/square_joists_x.gif) S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | 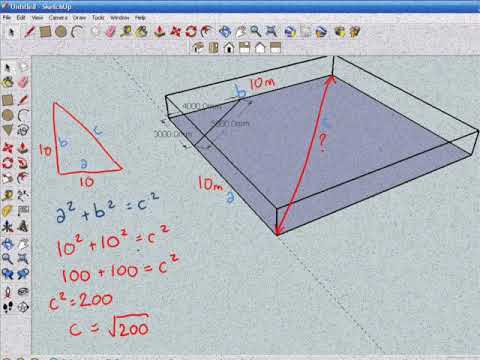 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | 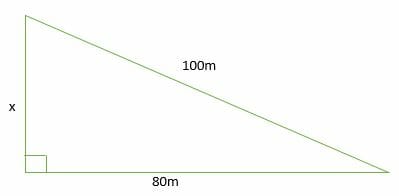 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
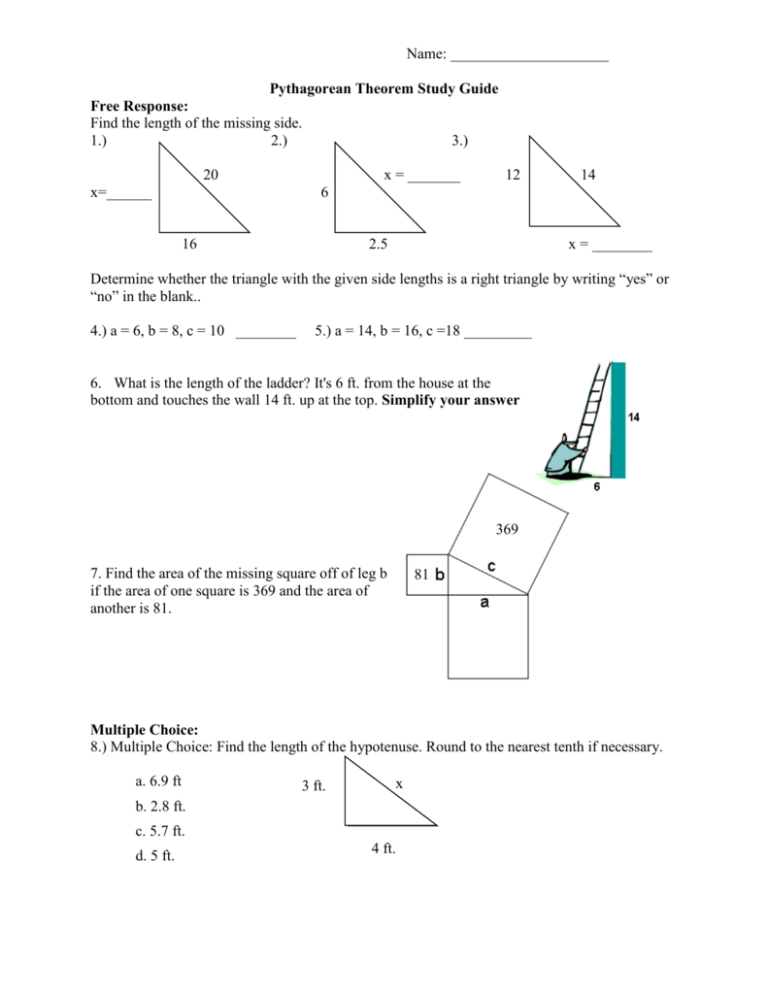 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | 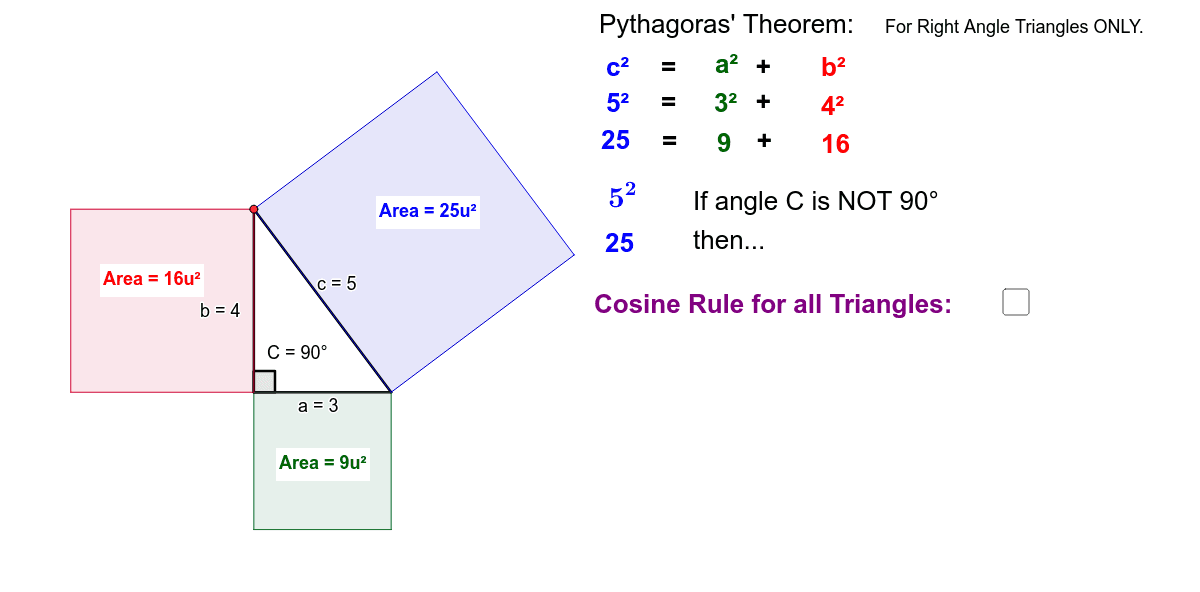 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | 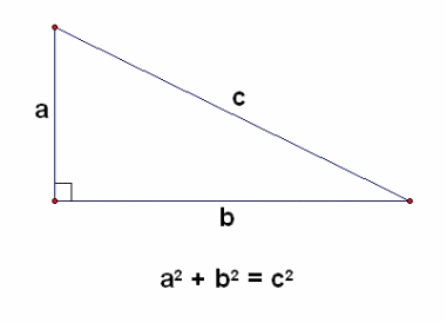 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | 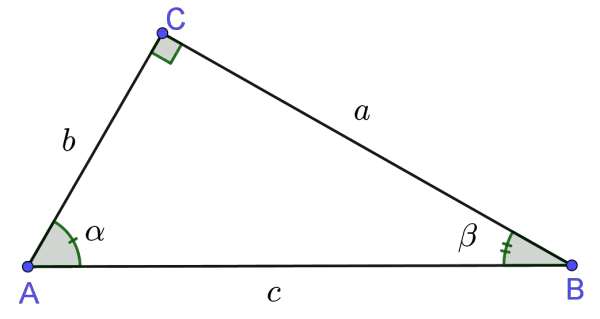 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | 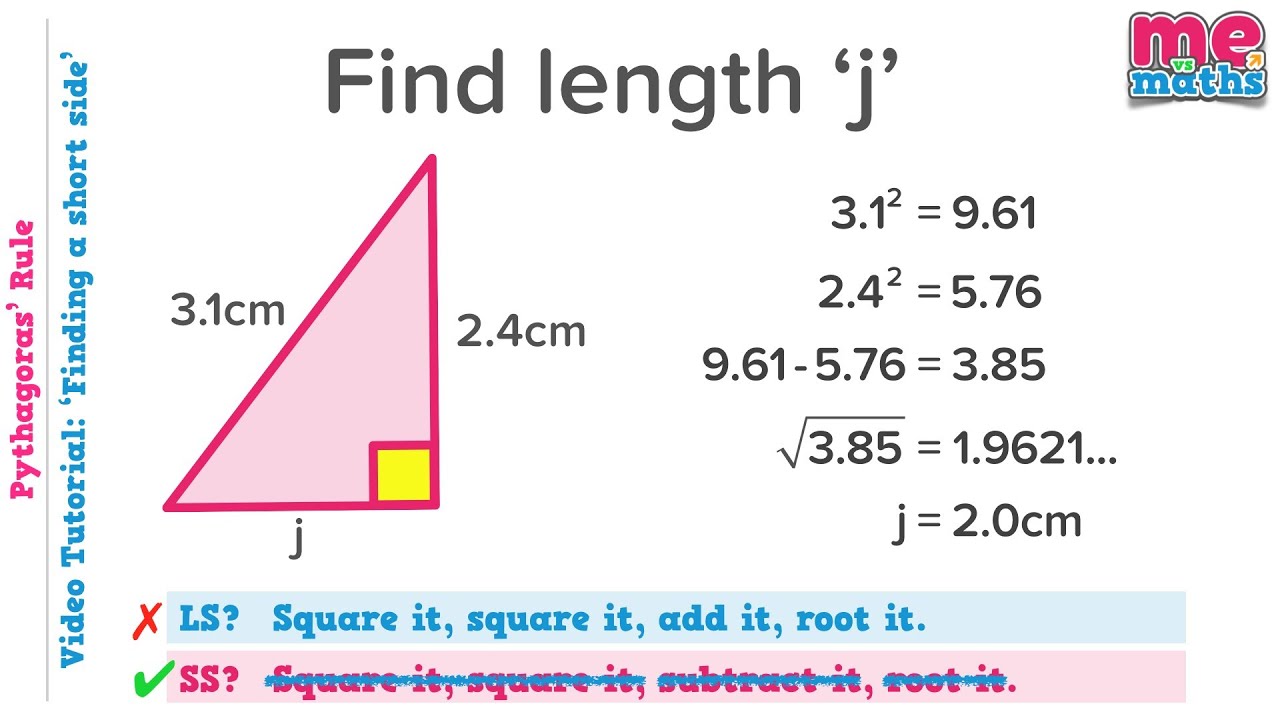 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | 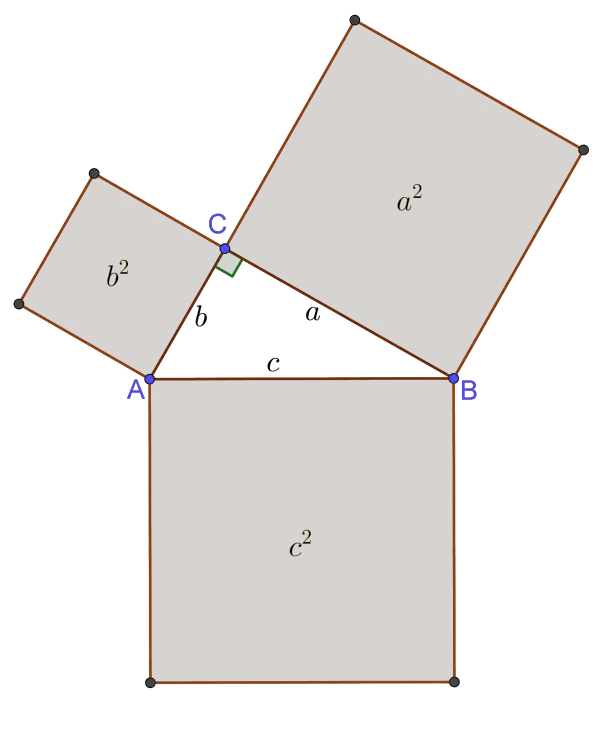 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | 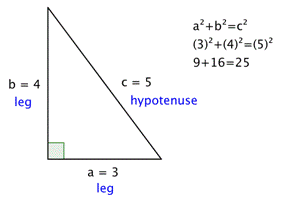 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
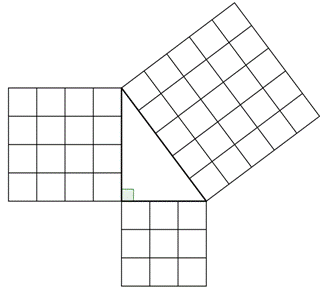 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | 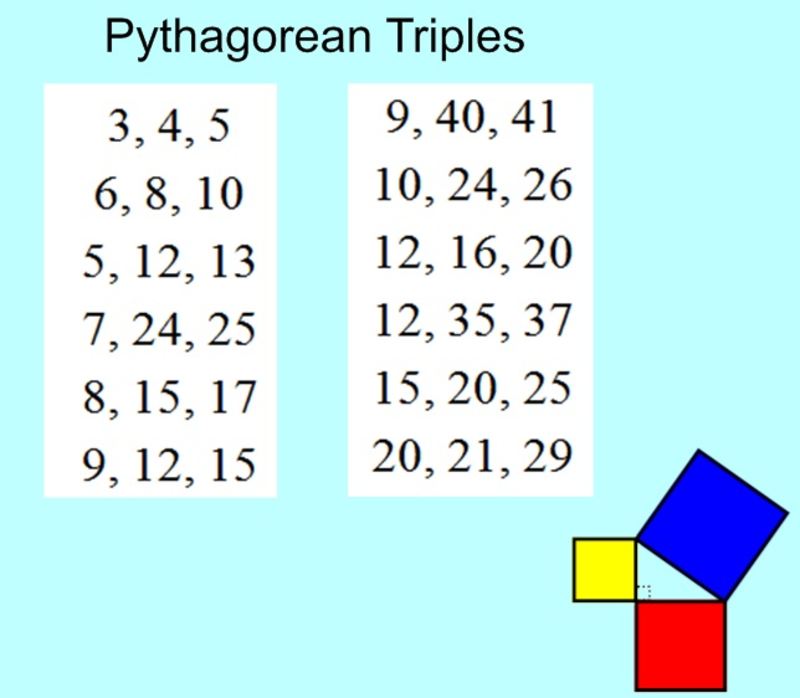 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
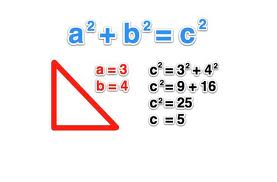 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | 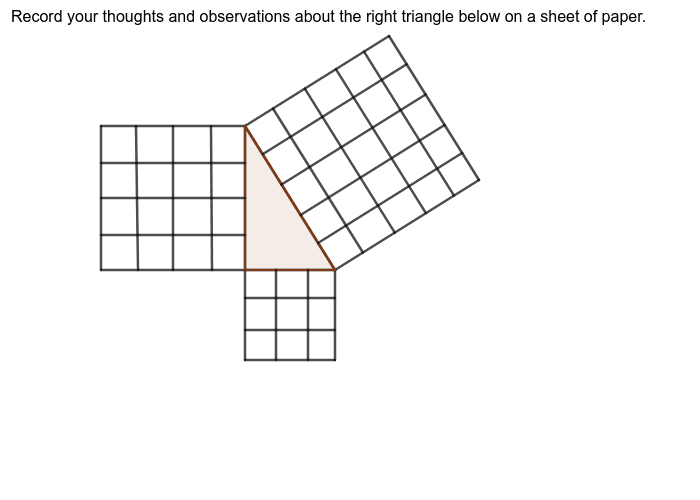 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | 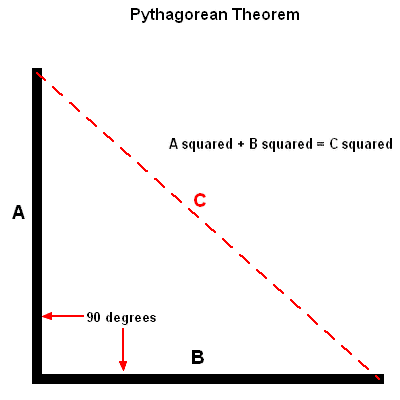 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
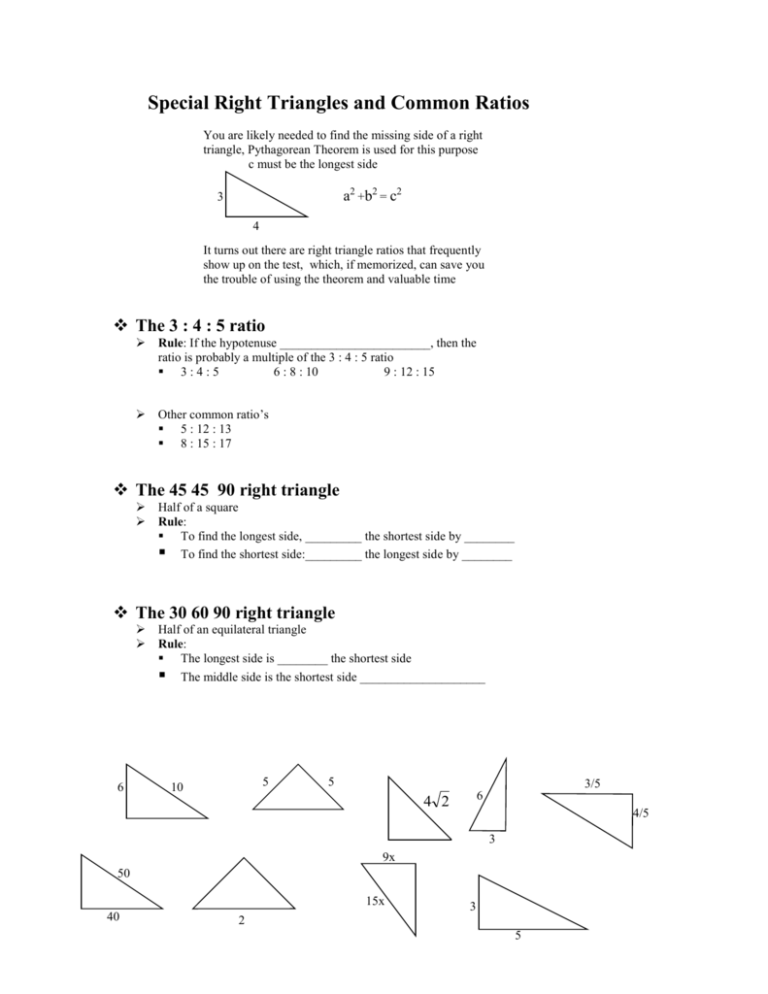
 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | 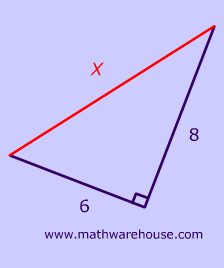 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
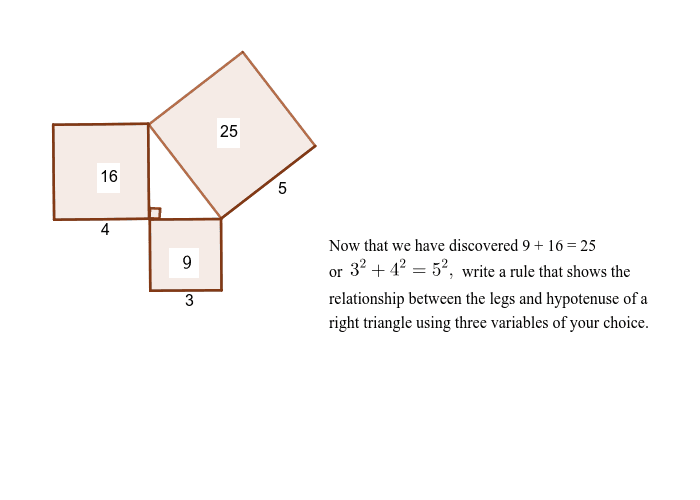 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | 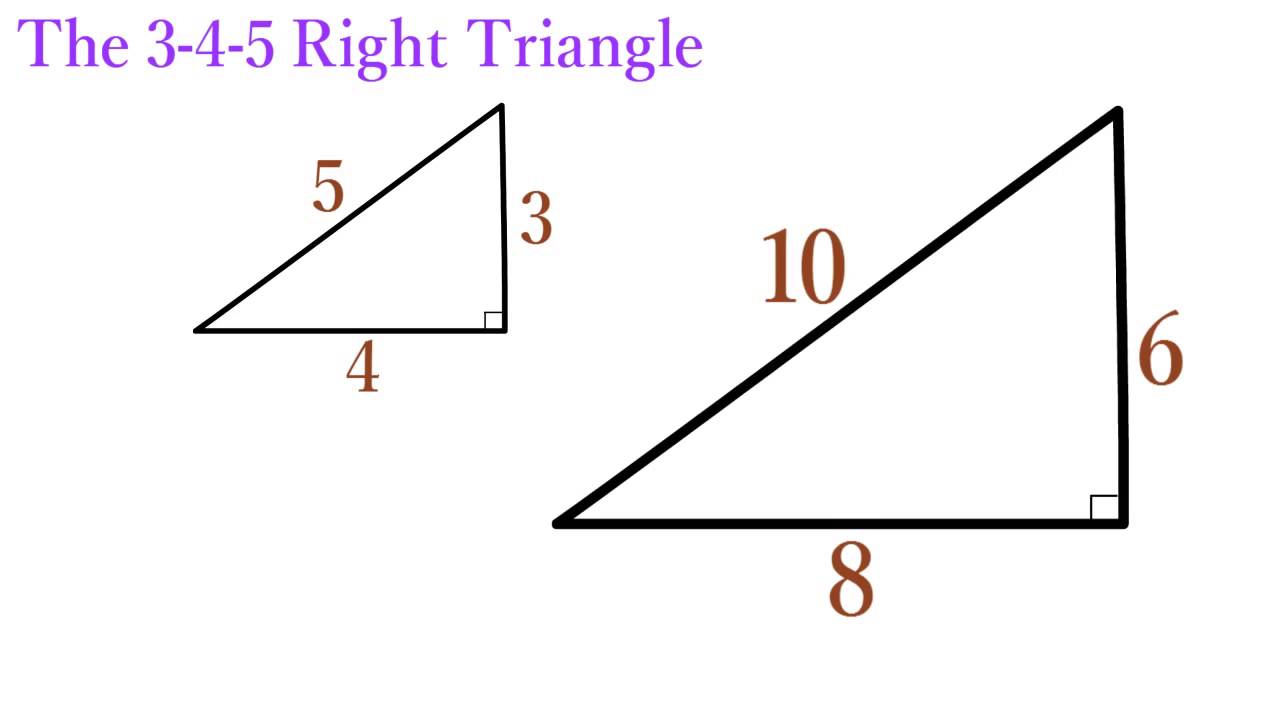 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | 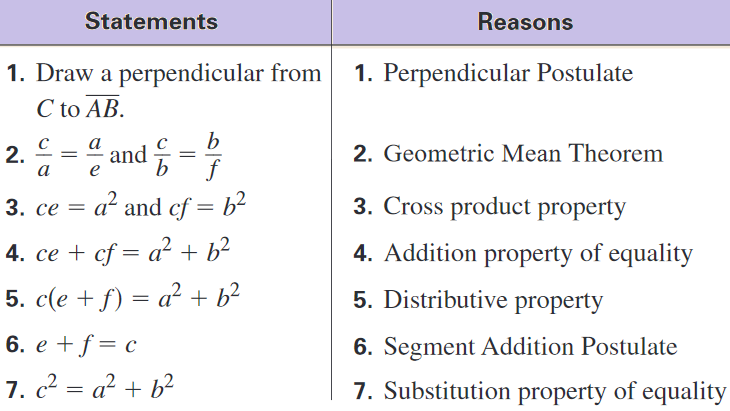 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | 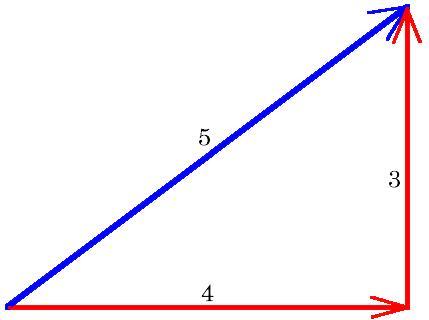 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | 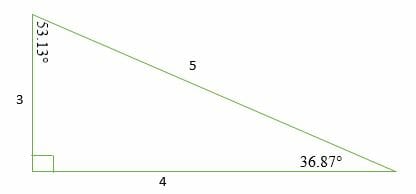 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem | 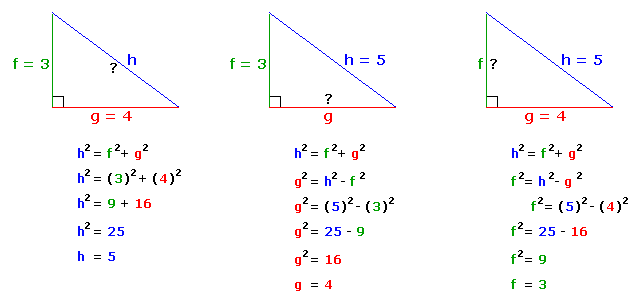 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
 S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |  S T E M The Pythagorean Theorem |
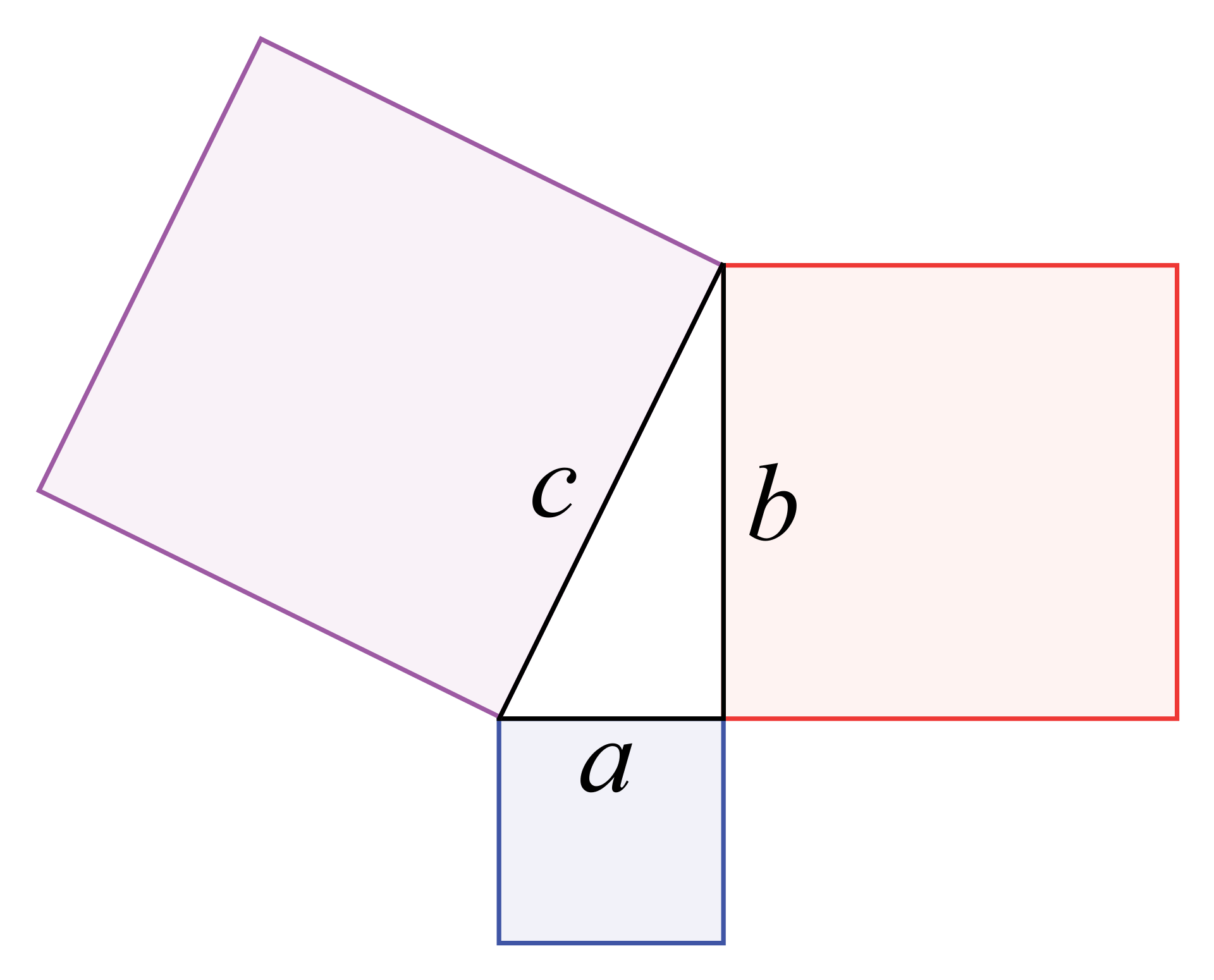
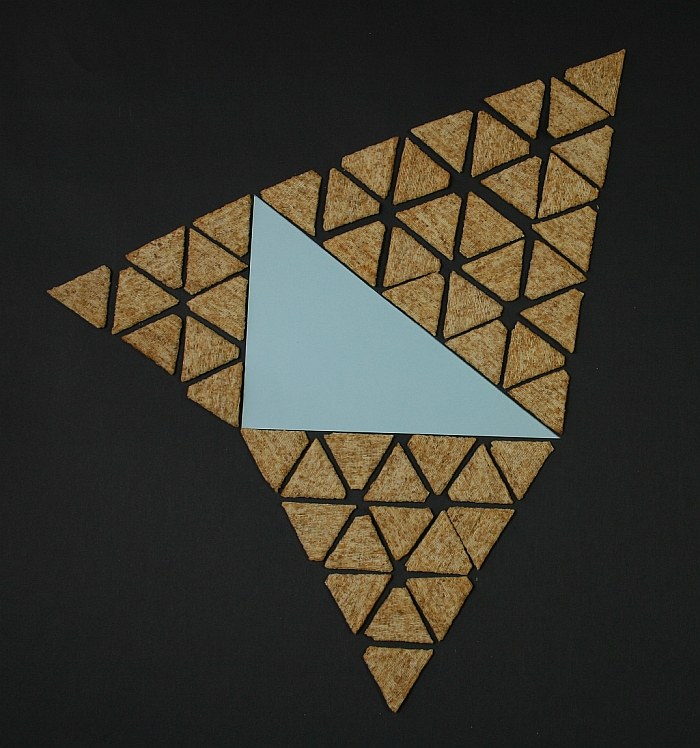
In Geometry, a well known method of constructing a right angle is to employ the Pythagorean TheoremPythagorean Theorem The Pythagorean Theorem, also known as Pythagoras' theorem, is a fundamental relation between the three sides of a right triangle Given a right triangle, which is a triangle in which one of the angles is 90°, the Pythagorean theorem states that the area of the square formed by the longest side of the right triangle (the hypotenuse) is equal to the sum of
Incoming Term: pythagorean theorem 3 4 5 rule, pythagorean theorem and 3 4 5 rule,




0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿